A Setting Technique for Comparative Protein Modelling for Web based SMART Tool
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10691316Keywords:
smart tool, protein, pssm, aluncAbstract
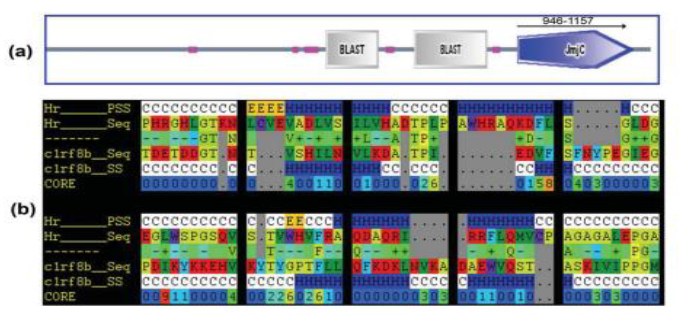
When the "hairless protein" linked to the hairless gene, which is necessary for hair growth, stops working, the result will be total hairlessness. This gene is located on chromosome 8 at locations 22027873-22045326. The hairless gene, which similarly aids in histone demethylation, is a member of the JmjC domain superfamily. With 1189 residues in the hairless protein, the domain sequence spans positions 946 to 1157 and is 212 amino acids long. JmjC domains have been identified in over 100 bacterial and eukaryotic sequences due to significant sequence similarity. Among them the human hairless gene, which is mutated in alopecia universalis sufferers. We have attempted to use the bioinformatics method to homology model the JmjC domain in the hairless protein. The tools and programmes used in this work are NCBI-BLASTP, EBIClustalW, SMART, 3D-PSSM, DeepView/Switzerland-PDB Viewer, PyMOL, and WhatCheck. The structure of the JmjC domain is predicted using the template crystal structure of the probable antibiotic biosynthesis protein from Thermus thermophilus HB8. The minimised energy value of the modelled domain structure was -3394.570 KJ/mol. The WHAT IF-Proteins Model Check tool was used to verify the simulated domain structure.
Downloads
References
Beaudoin, G.M., and Potter, G.B. Third: Chen, S.H., DeRenzo, C.L., Zarach, J.M., & Thompson, C.C. (2001). A new nuclear receptor corepressor is encoded by the hairless gene, which is mutated in congenital hair loss syndromes. Development and Genes., 15(20), 2687-701.
Van Steensel, M., Smith, F.J., Steijlen, P.M., Kluijt, I., Stevens, H.P., Messenger, A., Kremer, H., Dunnill, M.G., Kennedy, C., Munro, C.S., Doherty, V.R., McGrath, J.A., Covello, S.P., & Coleman, C. (1999). The hr gene was excluded by cDNA and genomic sequencing, and the gene for hypotrichosis of Marie Unna is located between D8S258 and D8S298. Journal of American Human Genetics, 65(2), 413-419.
Ahmad, W., John, P., Aslam, M., Rafiq, M.A., Amin-ud-din, M., & S. (2005). Two consanguineous Pakistani families had atrichia with papular lesions brought on by mutations in the human hairless gene. in: Archives of Dermatological Research, 297(5).
Wadhwa, G., Prakash, A., & Bhagavathi, S. (2012). An in-silico method to assess the evolutionary relationships of important proteins involved in lung cancer. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science, 2(11), 084-091.
Arul, L., Balasubramanian, P., Mohan, T.M., Jayakanthan, M., Wadhwa, G., & Sundar, D. (2009). Medication design employing computer assistance for the cancer-causing H-Ras p21 mutant protein. Drug Design and Discovery Letters, 6(1), 14–20.
Wadhwa, G., Khan, A.U., & Baig, M.H. (2011). Analysis of interactions between newly discovered SHV-variants and new generation cephalosporins using molecular docking. Bioinformation, 5(8), 331-335.
S.F. Altschul, W. Gish, W. Miller, E.W. Myers, & D.J. Lipman. (1990). Simple tool for local alignment searches. Molecular Biology Journal, 215(3), 403–410.
Copley, R.R., Doerks, T., Ponting, C.P., & Bork Schultz, J. (2000). A web-based tool for researching genetically mobile domains is called SMART. Research on Nucleic Acids, 28(1), 231–234.
Gibson, T.J., Higgins, D.G., & Thompson, J.D. (1994). Through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties, and weight matrix selection, CLUSTAL W increases the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment. Nucleic Acids Research, 22(22), 4673-468.
Sternberg, M.J., MacCallum, R.M., & Kelley, L.A. (2000). The 3D-PSSM program's structural characteristics are used to enhance genomic annotation. Molecular Biology Journal, 299(2), 499-520.
N. Guex and M.C. Peitsch. (1997). The Swiss-PdbViewer and SWISS-MODEL: A setting for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis, 18(15), 2714-2723.
Verma, D.K., Gautam, B., Singh, N., Kanojia, H., Singh, S., & Wadhwa, G. (2013). Streptococcus pyogenes metabolic pathway analysis was used to estimate the structure of the drug target. Journal of Biological Science and Bioinformatics International, 1(1), 79-85.
Vriend, G. (1990). A molecular modeling and drug development program WHAT IF. Molecular Graphics Journal, 8(1), 52–56.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
ARK
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Mohd. Azyumardi Azra

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Research Articles in 'Applied Science and Biotechnology Journal for Advanced Research' are Open Access articles published under the Creative Commons CC BY License Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. This license allows you to share – copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format. Adapt – remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.










