A Study on Factors Attributed to Failure of Pharmaceutical Products
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10976869Keywords:
pharma marketing, pharma crisis, pharma products, pharmaceutical industry, product withdrawalAbstract
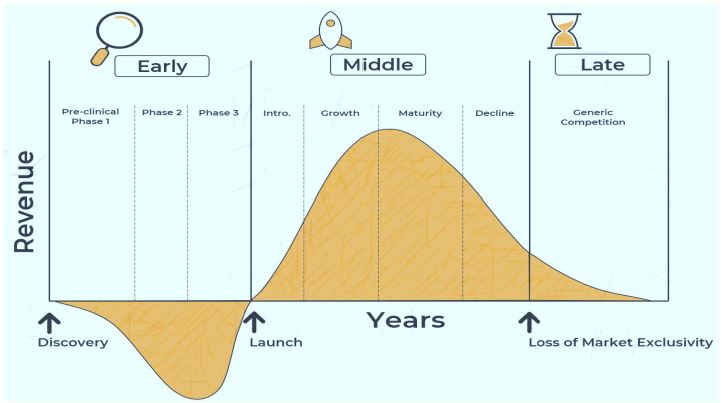
The Pharmaceutical Industry plays a pivotal role in healthcare by developing, manufacturing, and marketing drugs to treat a myriad of medical conditions. However, despite rigorous research, development, and testing processes, a significant number of pharmaceutical products fail to meet the expected standards or gain market acceptance. This study aims to explore the multifaceted factors that contribute to the failure of pharmaceutical products, focusing on the product life cycle as a framework for analysis. The product life cycle of a pharmaceutical product encompasses several stages, including research and development, clinical trials, regulatory approval, launch, and post-marketing surveillance. At each stage, various factors can influence the success or failure of a product. These factors range from scientific challenges and regulatory hurdles during the R&D phase to manufacturing issues, competitive pressures, and post-market safety concerns.
Through a comprehensive theoretical reviews and authors understanding of the subject, this study identifies key factors attributed to the failure of pharmaceutical products. These include but are not limited to Scientific Challenges: Inherent complexities in drug discovery and development, including target identification, drug design, and optimization, can lead to unforeseen efficacy or safety issues. Regulatory Hurdles: Stringent regulatory requirements and evolving guidelines can delay approvals, increase development costs, and limit market access for new drugs. Manufacturing Issues: Quality control failures, supply chain disruptions, and manufacturing inconsistencies can compromise the integrity, efficacy, and safety of pharmaceutical products. Competitive Pressures: Intense competition from generic drugs, biosimilars, and innovative therapies can erode market share and profitability, especially for products with limited differentiation. Post-Market Safety Concerns: Adverse events, drug interactions, and long-term side effects discovered after product launch can result in recalls, litigation, and damage to the brand reputation. By understanding and addressing these factors proactively, pharmaceutical companies can mitigate risks, enhance product quality, and improve the likelihood of success throughout the product life cycle. This study underscores the importance of comprehensive risk management, continuous monitoring, and adaptive strategies to navigate the complexities and challenges inherent in the pharmaceutical industry.
Downloads
References
Levy R. (1994). The role and value of pharmaceutical marketing. Arch Fam Med., 3(4), 327–32.
Khan MdMR, & Basak K. (2021). Shifts in pharma-marketing trends in post covid-19 era. International Journal of Multidisciplinary: Applied Business and Education Research, 2(2), 108–14.
Kosenko YuM, Ostapiv N V., Buchko OM, & Zaruma LE. (2023). Factors affecting the withdrawal period of amoxicillin from veterinary medicinal products used in food-producing animals. Scientific and Technical Bulletin оf State Scientific Research Control Institute of Veterinary Medical Products and Fodder Additives аnd Institute of Animal Biology, 24(2), 77–91.
Fung M, Thornton A, Mybeck K, Wu JHH, Hornbuckle K, & Muniz E. (2001). Evaluation of the characteristics of safety withdrawal of prescription drugs from worldwide pharmaceutical markets-1960 to 1999. Drug Inf J., 35(1), 293–317.
Onakpoya IJ, Heneghan CJ, & Aronson JK. (2018). Post-marketing withdrawal of analgesic medications because of adverse drug reactions: a systematic review. Expert Opin Drug Saf., 17(1), 63–72.
Martin JH. (2020). Effect of pharmaceutical regulatory policy on health impact. Br J Clin Pharmacol., 86(12), 2335–7.
Bruccoleri M, Perrone G, Mazzola E, & Handfield R. (2019). The magnitude of a product recall: offshore outsourcing vs. captive offshoring effects. Int J Prod Res., 57(13), 4211–27.
Pharmaceutical industry. [cited 2024 Mar 5]. Available from: https://www.britannica.com/technology/pharmaceutical-industry.
Bruhn JF, Scapin G, Cheng A, Mercado BQ, Waterman DG, & Ganesh T, et al. (2021). Small molecule microcrystal electron diffraction for the pharmaceutical industry–Lessons learned from examining over fifty samples. Front Mol Biosci., 8.
Daka Nagarjuna Reddy, Mahaveer Singh, Birendra Shrivastava, & Ravi Kumar Konda. (2020). Regulatory compliances in development of commercial scale process of Nanoparticles (Liposomes and Niosomes) in pharmaceutical industry : A review. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 11(4), 7094–101.
Jindal D, Kaur H, Patil RK, & Patil HC. (2020). Validation – In pharmaceutical industry: Equipment validation: A brief review. Adesh University Journal of Medical Sciences & Research, 2, 94.
Buonansegna E, Salomo S, Maier AM, & Li‐Ying J. (2014). Pharmaceutical new product development: why do clinical trials fail?. R&D Management, 44(2):189–202.
Ponnusamy SK, & Ragini YP. (2019). Product lifecycle in the pharmaceutical industry, pp. 112–32.
Prajapati V, Tripathy S, & Dureja H. (2013). Product lifecycle management through patents and regulatory strategies. Journal of Medical Marketing: Device, Diagnostic and Pharmaceutical Marketing, 13(3), 171–80.
Cahaya N, Rachma Pramestutie H, Kumala Hati A, & Utami P. (2022). Insurance, policy, knowledge level and epidemiology as factors affecting demand and supply of pharmaceutical product. Pharmaceutical Journal of Indonesia, 7(2), 79–88.
Tripathy S, Prajapati V, & Guruswamy VS. (2015). Product life cycle management for pharmaceutical innovation. Applied Clinical Research, Clinical Trials and Regulatory Affairs, 2(3), 145–52.
Vargesson N, & Stephens T. (2021). Thalidomide: history, withdrawal, renaissance, and safety concerns. Expert Opin Drug Saf, 20(12), 1455–7.
Wang Z, Richter SM, Gates BD, & Grieme TA. (2012). Safety concerns in a pharmaceutical manufacturing process using dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) as a solvent. Org Process Res Dev., 16(12), 1994–2000.
Löfgren H. (2007). The global biopharma industry and the rise of Indian drug multinationals: implications for Australian generics policy. Aust New Zealand Health Policy, 4(1), 10.
Rangi P, Marra C, Scahill S, & Anwar M. (2023). Impact of promotional videos on public perception of pharmacy services. J Pharm Pract, 089719002311772.
Moynihan R. (2002). Marketing: Celebrity selling---part two. BMJ, 325(7358), 286–286.
Novartis’ Beovu safety woes could cost billions of dollars, says analyst. [cited 2024 Mar 5]. Available from: https://pharmaphorum.com/news/novartis-beovu-launch-could-be-hit-by-safety-warning.
Novartis calls off 3 Beovu trials testing more frequent dosing on concerns of vision-threatening side effect. [cited 2024 Mar 5]. Available from: https://www.fiercepharma.com/marketing/novartis-takes-its-eyes-off-3-beovu-trials-more-frequent-dosing-safety-concerns.
Beovu update: No recall yet, but 3 clinical trials have been terminated. [cited 2024 Mar 5]. Available from: https://www.jdsupra.com/legalnews/beovu-update-no-recall-yet-but-3-2210097/.
Beovu lawsuit. [cited 2024 Mar 5]. Available from: https://www.millerandzois.com/products-liability/drugs/beovu-lawsuits/.
Beovu lawsuit update. [cited 2024 Mar 5]. Available from: https://www.drugwatch.com/beovu/lawsuits/.
The dengue vaccine dilemma. [cited 2024 Mar 5]. Available from: https://www.pharmaceutical-technology.com/features/dangvaxia-philippines/.
Dengue vaccine fiasco leads to criminal charges for researcher in the Philippines. [cited 2024 Mar 5]. Available from: https://www.science.org/content/article/dengue-vaccine-fiasco-leads-criminal-charges-researcher-philippines.
Seema Yasmin & Madhusree Mukerjee. Is a runaway immune reaction making a dengue vaccine dangerous?. [cited 2024 Mar 5]. Available from: https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/how-the-worlds-first-dengue-vaccination-drive-ended-in-disaster/.
Arham AF, Amin L, Mustapa MAC, Mahadi Z, Yaacob M, & Arham AF, et al. (2022). “To do, or not to do?”: determinants of stakeholders’ acceptance on dengue vaccine using PLS-SEM analysis in Malaysia. BMC Public Health, 22(1), 1574.
How can pharmaceutical companies meet drug launch expectations. [cited 2024 Mar 5]. Available from: https://pharmanewsintel.com/features/how-can-pharmaceutical-companies-meet-drug-launch-expectations.
Aiming to avoid Pfizer’s Eucrisa failure, Arcutis wins FDA nod for Zoryve cream in psoriasis. [cited 2024 Mar 5]. Available from: https://www.fiercepharma.com/marketing/aiming-avoid-pfizers-eucrisa-failure-arcutis-wins-fda-nod-zoryve-cream-psoriasis.
Zoryve cream by arcutis receives fda approval for psoriasis. [cited 2024 Mar 5]. Available from: https://www.worldpharmatoday.com/news/zoryve-cream-by-arcutis-receives-fda-approval-for-psoriasis/.
Bou Zerdan M, Bidikian AH, Alameh I, Nakib C El, & Assi HI. (2021). Olaratumab’s failure in soft tissue sarcoma. Rare Tumors, 13, 203636132110341.
Acadia’s Nuplazid gets FDA expanded use review, fails phase 3 depression trial. [cited 2024 Mar 7]; Available from: https://www.spglobal.com/marketintelligence/en/news-insights/latest-news-headlines/acadia-s-nuplazid-gets-fda-expanded-use-review-fails-phase-3-depression-trial-59502768.
Acadia’s Nuplazid fails to prove effectiveness in schizophrenia trial. [cited 2024 Mar 7]; Available from: https://www.biospace.com/article/acadia-pharma-s-parkinson-s-drug-nuplazid-drug-flunks-clinical-trial-for-schizophrenia/.
Acadia Pharma drug fails to improve psychosis in schizophrenia patients. [cited 2024 Mar 7]; Available from: https://www.statnews.com/2019/07/22/acadia-pharma-drug-fails-to-improve-psychosis-in-schizophrenia-patients/.
Acadia fails in attempt to expand use of antipsychotic to treat patients with depression. [cited 2024 Mar 7]; Available from: https://www.statnews.com/2020/07/20/acadia-nuplazid-major-depression/.
Ocaliva fails NASH trial just as Intercept charts path toward FDA application. [cited 2024 Mar 7]; Available from: https://www.fiercepharma.com/pharma/ocalivas-2nd-nash-trial-bites-dust-just-intercept-charts-path-fda-re-application.
Intercept to abandon NASH research, lay off staff after FDA drug rejection. [cited 2024 Mar 7]; Available from: https://www.biopharmadive.com/news/intercept-fda-rejection-nash-oca-restructuring/653751/.
Intercept’s NASH dreams may be dashed after FDA panel votes against Ocaliva’s approval bid. [cited 2024 Mar 7]; Available from: https://www.fiercepharma.com/pharma/intercepts-nash-dreams-crash-after-fda-expert-panel-votes-against-ocalivas-benefit-risk.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
ARK
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Alkesh S. Mourya, Dr. Rajesh Kumar Pandey

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Research Articles in 'Applied Science and Biotechnology Journal for Advanced Research' are Open Access articles published under the Creative Commons CC BY License Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. This license allows you to share – copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format. Adapt – remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.










