Understanding Insulin Mechanisms, Economic Implications, and Future Prospects
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.11761361Keywords:
diabetes, insulin, economics, bio-similars, insulin-analogue, insulin mechanisn, insulin-biosynthesisAbstract
Diabetes, a persistent metabolic challenge affecting various organs,are of three primary types—Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational—stemming from intricate interplays of genetics and environment. On a global scale, 537 million adults grapple with diabetes, with India experiencing a growing burden. The vital role of insulin in glucose regulation involves a complex biosynthesis process. Economic hurdles, compounded by soaring insulin prices, call for policy interventions to ensure accessible healthcare. Diverse insulin types cater to distinct patient needs, while biosimilars, like the FDA-approved Semglee, offer affordability. Economic analyses underscore the advantages of biosimilars, highlighting the dynamic landscape of diabetes management and treatment costs.
Downloads
References
G. Roglic. (2016). ‘WHO global report on diabetes: A summary. Int J Noncommun Dis, 1(1), 3. doi:10.4103/2468-8827.184853.
M. Stumvoll, B. J. Goldstein, & T. W. van Haeften. (2005). Type 2 diabetes: principles of pathogenesis and therapy. The Lancet, 365(9467), 1333–1346. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)61032-X.
D. M. Muoio, & C. B. Newgard. (2008). Molecular and metabolic mechanisms of insulin resistance and β-cell failure in type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 9(3), 193–205. doi:10.1038/nrm2327.
U. Galicia-Garcia et al. (2020). Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Mol Sci, 21(17), 6275. doi:10.3390/ijms21176275.
P. M. Catalano. (2014). Trying to understand gestational diabetes. Diabetic Medicine, 31(3), 273–281. doi:10.1111/dme.12381.
A. Kumar, R. Gangwar, A. Ahmad Zargar, R. Kumar, & A. Sharma. (2024). Prevalence of diabetes in India: A review of IDF diabetes atlas 10th edition. Curr Diabetes Rev, 20(1). doi:10.2174/1573399819666230413094200.
R. A. Haeusler, T. E. McGraw, & D. Accili. (2018). Biochemical and cellular properties of insulin receptor signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 19(1), 31–44. doi:10.1038/nrm.2017.89.
P. Rorsman, & M. Braun. (2013). Regulation of insulin secretion in human pancreatic islets. Annu Rev Physiol, 75(1), 155–179. doi:10.1146/annurev-physiol-030212-183754.
Z. Fu, E. R. Gilbert, & D. Liu. (2013). Regulation of insulin synthesis and secretion and pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction in diabetes. Curr Diabetes Rev, 9(1), 25–53.
A. De Vos et al. (1995). Human and rat beta cells differ in glucose transporter but not in glucokinase gene expression. J Clin Invest, 96(5), 2489–95. doi:10.1172/JCI118308.
B. Bansode, & D. S. Jungari. (2019). Economic burden of diabetic patients in India: A review. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, 13(4), 2469–2472. doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2019.06.020.
M. S. Rahman et al. (2021). Role of insulin in health and disease: An update. Int J Mol Sci, 22(12), 6403. doi:10.3390/ijms22126403.
B. B. Davidovici et al. (2010). Psoriasis and systemic inflammatory diseases: Potential mechanistic links between skin disease and co-morbid conditions. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 130(7), 1785–1796. doi:10.1038/jid.2010.103.
M. V. Plikus et al. (2015). The circadian clock in skin. J Biol Rhythms, 30(3), 163–182. doi:10.1177/0748730414563537.
E. Baselga Torres, & M. Torres-Pradilla. (2014). Manifestaciones cutáneas en niños con diabetes mellitus y obesidad. Actas Dermosifiliogr, 105(6), 546–557. doi:10.1016/j.ad.2013.11.014.
F. S. Hough, D. D. Pierroz, C. Cooper, S. L. Ferrari, & __. (2016). Mechanisms in endocrinology: Mechanisms and evaluation of bone fragility in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Eur J Endocrinol, 174(4), R127–R138. doi:10.1530/EJE-15-0820.
A. R. Saltiel. (2021). Insulin signaling in health and disease. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 131(1). doi:10.1172/JCI142241.
R. Pradeepa, & V. Mohan. (2021). Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes in India. Indian J Ophthalmol, 69(11), 2932. doi:10.4103/ijo.IJO_1627_21.
B. Bansode, & D. S. Jungari. (2019). Economic burden of diabetic patients in India: A review. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, 13(4), 2469–2472. doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2019.06.020.
W. H. Herman, & S. Kuo. (2021). 100 years of insulin: Why is insulin so expensive and what can be done to control its cost?. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am, 50(3), e21–e34. doi:10.1016/j.ecl.2021.09.001.
K. Ahmad. (2014). Insulin sources and types: a review of insulin in terms of its mode on diabetes mellitus. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 34(2), 234–237. doi:10.1016/S0254-6272(14)60084-4.
D. Gotham, M. J. Barber, & A. Hill. (2018). Production costs and potential prices for biosimilars of human insulin and insulin analogues. BMJ Glob Health, 3(5), e000850. doi:10.1136/bmjgh-2018-000850.
G. Sutton, J. Minguet, C. Ferrero, & P. Bramlage. (2014). U300, a novel long-acting insulin formulation. Expert Opin Biol Ther, 14(12), 1849–1860. doi:10.1517/14712598.2014.970633.
K. D. Niswender. (2011). Basal insulin: Physiology, pharmacology, and clinical implications. Postgrad Med, 123(4), 17–26. doi:10.3810/pgm.2011.07.2300.
G. B. Bolli, & D. R. Owens. (2000). Insulin glargine. The Lancet, 356(9228), 443–445. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02546-0.
M. C. Jones, & M. Patel. (2006). Insulin detemir: A long-acting insulin product. American Journal of Health-System Pharmacy, 63(24), 2466–2472. doi:10.2146/ajhp060102.
P. Lucidi et al. (2015). Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of NPH insulin in type 1 diabetes: The importance of appropriate resuspension before subcutaneous injection. Diabetes Care, 38(12), 2204–2210. doi:10.2337/dc15-0801.
M. Norrman, F. Hubálek, & G. Schluckebier. (2007). Structural characterization of insulin NPH formulations. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 30(5), 414–423. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2007.01.003.
S. F, & S. A. (2024). NPH insulin. Accessed: Mar. 25, 2024. [Online]. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31751050/.
Diabetes treatment: Using insulin to manage blood sugar - Mayo clinic. Accessed: Mar. 25, 2024. [Online]. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/in-depth/diabetes-treatment/art-20044084.
Insulin - StatPearls - NCBI bookshelf. Accessed: Mar. 25, 2024. [Online]. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560688/.
K. F. S. Melo et al. (2019). Short-acting insulin analogues versus regular human insulin on postprandial glucose and hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetol Metab Syndr, 11(1), 2. doi:10.1186/s13098-018-0397-3.
About short-acting insulin - NHS. Accessed: Mar. 25, 2024. [Online]. Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/insulin/short-acting-insulin/about-short-acting-insulin/.
Insulin basics. ADA. Accessed: Mar. 25, 2024. [Online]. Available at: https://diabetes.org/health-wellness/medication/insulin-basics.
Bolus insulins (Short-acting and rapid-acting) - The Johns Hopkins patient guide to diabetes. Accessed: Mar. 25, 2024. [Online]. Available at: https://hopkinsdiabetesinfo.org/medications-for-diabetes-regular-and-rapid-acting-insulins/.
H. W. Rodbard, & D. Rodbard. (2020). Biosynthetic human insulin and insulin analogs. Am J Ther, 27(1), e42–e51. doi:10.1097/MJT.0000000000001089.
M. Weiss, D. F. Steiner, & L. H. Philipson. (2000). Insulin biosynthesis, secretion, structure, and structure-activity relationships. Endotext. Accessed: Mar. 25, 2024. [Online]. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25905258/.
A. Permutt, J. Chirgwin, S. Giddings, K. Kakita, & P. Rotwein. (1981). Insulin biosynthesis and diabetes mellitus. Clin Biochem, 14(5), 230–236. doi:10.1016/S0009-9120(81)90940-1.
Insulin analogs - Diabetes education online. Accessed: Mar. 25, 2024. [Online]. Available at: https://dtc.ucsf.edu/types-of-diabetes/type2/treatment-of-type-2-diabetes/medications-and-therapies/type-2-insulin-rx/types-of-insulin/insulin-analogs/.
Biosimilar insulin treatment: What the science says. Endocrine Society. Accessed: Mar. 25, 2024. [Online]. Available at: https://www.endocrine.org/patient-engagement/hormone-headlines-blog/biosimilar-insulin-treatment.
Biosimilar insulins – What you need to know. Accessed: Mar. 25, 2024. [Online]. Available at: https://jdrf.ca/biosimilar-insulins-what-you-need-to-know/.
What is biosimilar insulin?. Accessed: Mar. 25, 2024. [Online]. Available at: https://beyondtype1.org/what-is-biosimilar-insulin-resource/.
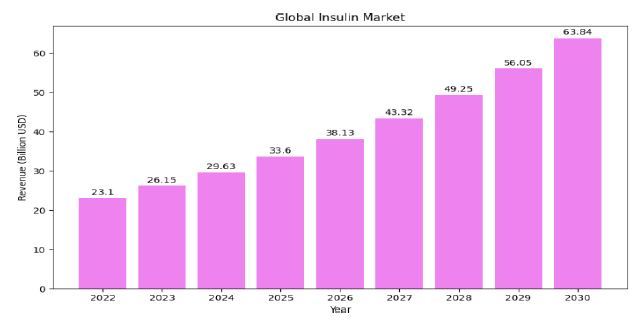
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
ARK
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Dr. Lingayya Hiremath, Yashvi Tripathi, Srujan Shetty, Priyadarshini J, Pramod K B

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Research Articles in 'Applied Science and Biotechnology Journal for Advanced Research' are Open Access articles published under the Creative Commons CC BY License Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. This license allows you to share – copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format. Adapt – remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.










