Adversarial for Sequential Recommendation Walking in the Multi-Latent Space
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.12803769Keywords:
sequential recommendation, adversarial learning, interpretabilityAbstract
Recently, sequential recommendation plays a critical role in our daily life, since it serves as personalized information filters to dis- cover popular users’ preferred products over time. Due to the success of the adversarial learning, a mass of research efforts start to strengthen sequential recommendation by the adversarial learning, which is able to learn complex underlying data distribution.
However, existing adversarial sequential recommendation methods suffer from mode collapse and unexplained prediction. To boost the diversity, performance, and interpretability of sequential recommendation system, we propose a novel temporal-aware adversarial framework, namely TSRGAN.
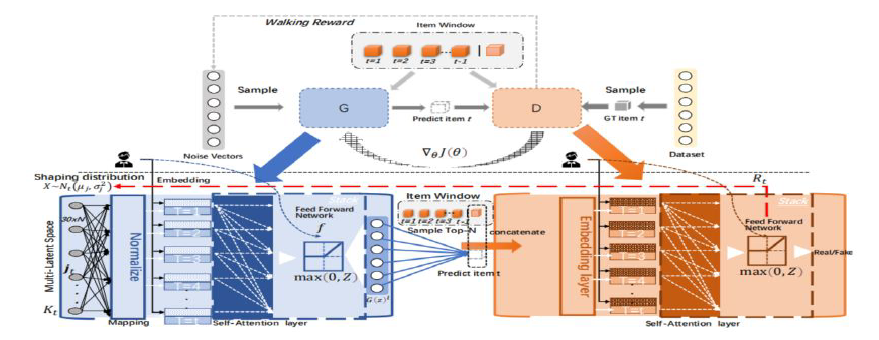
In principle, the input of traditional adversarial-based recommendation system is a noise variable sampled from normal distribution. We argue that it is hard to generate an item cover complex users’ preferences(e.g. price, brand and item style) using a single latent space. Therefore, our model employs multiple latent space to generate plausible item which matches user’ preferences from multiple views(e.g. Movie style, Movie release date).
Besides, previous adversarial-based recommenders focus on generating active item, but they omits that user’s favour is not in- variable. With GANs terminology, the recommenders only will be rewarded when seeking the peak mode, but it neglects minor mode, in other word mode collapse. In order to alleviate this issue, we design a novel diversity reward function and diversify regularization to encourage the model exploring minor mode over time and guarantee generating diversity item with reasonable.
Concretely, we propose multiple learnable latent codes to generate item matching user’s preferences from different views, then we leverage the diversity reward signal to shape the distribution of multiple latent space over time. It means that the multiple latent space are sampled form different distribution instead of Gaussian distribution. Such a manipulation of the latent space can be treated as walking from plain distribution latent space to diversity distributions latent space. Further, the reward signal is modified over time, therefore, our methods names "Temporal-aware" adversarial framework.
In short, our model has two sequential stages: encode the user’ characteristics and historical behaviours under multiple latent space with the Self Attention-based generator(G), and discriminator(D) try to distinguish the generator’s output item from the ground ruth. Besides, discriminator attempt to apply reward signal to shape the latent space distribution time by time. Extensive experiments demonstrate remarkable performance with interpretability improvement against the state-of-the-art baselines.
Downloads
References
Wang, Z., Yan, H., Wang, Y., Xu, Z., Wang, Z., & Wu, Z. (2024). Research on autonomous robots navigation based on reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.02539.
Wantlin, K., Wu, C., Huang, S. C., Banerjee, O., Dadabhoy, F., Mehta, V. V., ... & Rajpurkar, P. (2023). Benchmd: A benchmark for modality-agnostic learning on medical images and sensors. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.08486.
Li, Zhenglin, et al. (2023). Stock market analysis and prediction using LSTM: A case study on technology stocks. Innovations in Applied Engineering and Technology, 1-6.
Liu, Y., Yang, H., & Wu, C. (2023). Unveiling patterns: A study on semi-supervised classification of strip surface defects. IEEE Access, 11, 119933-119946.
Restrepo, D., Wu, C., Vásquez-Venegas, C., Nakayama, L. F., Celi, L. A., & López, D. M. (2024). DF-DM: A foundational process model for multimodal data fusion in the artificial intelligence era. Research Square.
Li, Shaojie, Yuhong Mo, & Zhenglin Li. (2022). Automated pneumonia detection in chest x-ray images using deep learning model. Innovations in Applied Engineering and Technology, 1-6.
Shovestul, B., Saxena, A., Reda, S., Dudek, E., Wu, C., Lamberti, J. S., & Dodell-Feder, D. (2022). Social affective forecasting and social anhedonia in schizophrenia-spectrum disorders: a daily diary study. Schizophrenia, 8(1), 97.
Restrepo, D., Wu, C., Cajas, S. A., Nakayama, L. F., Celi, L. A. G., & Lopez, D. M. (2024). Multimodal deep learning for low-resource settings: A vector embedding alignment approach for healthcare applications. medRxiv.
Wu, C., Yang, X., Gilkes, E. G., Cui, H., Choi, J., Sun, N., ... & Nakayama, L. (2023, October). De-identification and obfuscation of gender attributes from retinal scans. in Workshop on Clinical Image-Based Procedures, pp. 91-101. Cham: Springer Nature, Switzerland.
Mo, Y., Tan, C., Wang, C., Qin, H., & Dong, Y. (2024). Make scale invariant feature transform “Fly” with CUDA. International Journal of Engineering and Management Research, 14(3), 38-45.
Nakayama, L. F., Choi, J., Cui, H., Gilkes, E. G., Wu, C., Yang, X., ... & Celi, L. A. (2023). Pixel snow and differential privacy in retinal fundus photos de-identification. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 64(8), 2399-2399.
Cajas, S. A., Restrepo, D., Moukheiber, D., Kuo, K. T., Wu, C., Chicangana, D. S. G., ... & Celi, L. A. A multi-modal satellite imagery dataset for public health analysis in Colombia.
Moukheiber, D., Restrepo, D., Cajas, S. A., Montoya, M. P. A., Celi, L. A., Kuo, K. T., ... & Kuo, P. C. (2024). A multimodal framework for extraction and fusion of satellite images and public health data. Scientific Data, 11(1), 634.
Restrepo, D., Wu, C., Vásquez-Venegas, C., Matos, J., Gallifant, J., & Nakayama, L. F. (2024). Analyzing diversity in healthcare LLM research: A scientometric perspective. medRxiv.
He, Shuyao, et al. (2024). Lidar and monocular sensor fusion depth estimation. Applied Science and Engineering Journal for Advanced Research, 3(3), 20-26.
Lin, Z., & Xu, F. (2023, July). Simulation of robot automatic control model based on artificial intelligence algorithm. in 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Autonomous Robot Systems (AIARS), pp. 535-539. IEEE.
Lin, Z., Wang, Z., Zhu, Y., Li, Z., & Qin, H. (2024). Text sentiment detection and classification based on integrated learning algorithm. Applied Science and Engineering Journal for Advanced Research, 3(3), 27-33.
Mo, Yuhong, et al. (2024). Large Language Model (LLM) AI text generation detection based on transformer deep learning algorithm. International Journal of Engineering and Management Research, 14(2), 154-159.
Lin, Z., Wang, Z., Zhu, Y., Li, Z., & Qin, H. (2024). Text sentiment detection and classification based on integrated learning algorithm. Applied Science and Engineering Journal for Advanced Research, 3(3), 27-33.
Dai, S., Dai, J., Zhong, Y., Zuo, T., & Mo, Y. (2024). The cloud-based design of unmanned constant temperature food delivery trolley in the context of artificial intelligence. Journal of Computer Technology and Applied Mathematics, 1(1), 6-12.
Lin, Z., Wang, C., Li, Z., Wang, Z., Liu, X., & Zhu, Y. (2024). Neural radiance fields convert 2d to 3d texture. Applied Science and Biotechnology Journal for Advanced Research, 3(3), 40-44.
Zhan, D., Yi, S., Xu, D., Yu, X., Jiang, D., Yu, S., ... & Zhang, W. (2019). Adaptive transfer learning of multi-view time series classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.07632.
Zhan, D., Yi, S., & Jiang, D. (2018, November). Small-scale demographic sequences projection based on time series clustering and lstm. in IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW), pp. 803-809. IEEE
Yi, S., Zhan, D., Zhang, W., Jiang, D., An, K., & Wang, H. (2019). Fisgan: Gan with flow-based importance sampling. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.02519.
Mo, Yuhong, et al. (2024). Password complexity prediction based on roberta algorithm. Applied Science and Engineering Journal for Advanced Research 3(3), 1-5.
Gao, H., Li, Y., Long, K., Yang, M., & Shen, Y. (2024). A survey for foundation models in autonomous driving. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.01105.
Zhao, Y., & Gao, H. (2024). Utilizing large language models for information extraction from real estate transactions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.18043.
Liu, Tianrui, et al. (2024). Spam detection and classification based on distilbert deep learning algorithm. Applied Science and Engineering Journal for Advanced Research, 3(3), 6-10.
Zhan, D., Yi, S., Xu, D., Yu, X., Jiang, D., Yu, S., ... & Zhang, W. (2019). Adaptive transfer learning of multi-view time series classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.07632.
Zhan, D., Yi, S., & Jiang, D. (2018, November). Small-scale demographic sequences projection based on time series clustering and lstm-rnn. in IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW), pp. 803-809.
Yi, S., Zhan, D., Zhang, W., Jiang, D., An, K., & Wang, H. (2019). Fisgan: Gan with flow-based importance sampling. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.02519.
Hu, X., Sun, Z., Nian, Y., Wang, Y., Dang, Y., Li, F., ... & Tao, C. (2024). Self-explainable graph neural network for alzheimer disease and related dementias risk prediction: Algorithm development and validation study. JMIR Aging, 7(1), e54748.
Song, Jintong, et al. (2024). A comprehensive evaluation and comparison of enhanced learning methods. Academic Journal of Science and Technology, 10(3), 167-171.
Li, F., Rasmy, L., Xiang, Y., Feng, J., Abdelhameed, A., Hu, X., ... & Tao, C. (2024). Dynamic prognosis prediction for patients on DAPT after drug‐eluting stent implantation: Model development and validation. Journal of the American Heart Association, 13(3), e029900.
Liu, Tianrui, et al. (2024). Spam detection and classification based on distilbert deep learning algorithm. Applied Science and Engineering Journal for Advanced Research, 3(3), 6-10.
He, J., Li, F., Hu, X., Li, J., Nian, Y., Wang, J., ... & Tao, C. (2022, June). Chemical-protein relation extraction with pre-trained prompt tuning. in IEEE 10th International Conference on Healthcare Informatics (ICHI), pp. 608-609.
He, J., Li, F., Li, J., Hu, X., Nian, Y., Xiang, Y., ... & Tao, C. (2024). Prompt tuning in biomedical relation extraction. Journal of Healthcare Informatics Research, 8(2), 206-224.
Mo, Yuhong, et al. (2024). Prediction of heart failure patients based on multiple machine learning algorithms. Applied and Computational Engineering, 75, 1-7. doi:10.54254/2755-2721/75/20240498.
Zhang, Jingyu, et al. (2024). Research on detection of floating objects in river and lake based on AI image recognition. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Practice, 7(2), 97-106.
Xiang, Ao, et al. (2024). Research on splicing image detection algorithms based on natural image statistical characteristics. Journal of Image Processing Theory and Applications, 7(1), 43-52.
Yu Cheng, Qin Yang, Liyang Wang, Ao Xiang, & Jingyu Zhang. (2024). Research on credit risk early warning model of commercial banks based on neural network algorithm. Financial Engineering and Risk Management, 7, 11-19. doi:10.23977/ferm.2024.070402.
Xiang, Ao, et al. (2024). A neural matrix decomposition recommender system model based on the multimodal large language model. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.08942.
Zhu, Armando, et al. (2024). Cross-task multi-branch vision transformer for facial expression and mask wearing classification. Journal of Computer Technology and Applied Mathematics, 1(1), 46-53.
Li, Keqin, et al. (2024). Utilizing deep learning to optimize software development processes. Journal of Computer Technology and Applied Mathematics, 1(1), 70-76.
Li, Keqin, et al. (2024). The application of augmented reality (AR) in remote work and education. Journal of Computer Technology and Applied Mathematics, 1(1), 33-39.
Hong, Bo, et al. (2024). The application of artificial intelligence technology in assembly techniques within the industrial sector. Journal of Artificial Intelligence General Science (JAIGS), 5(1), 1-12.
Dai, Shuying, et al. (2024). AI-based NLP section discusses the application and effect of bag-of-words models and TF-IDF in NLP tasks. Journal of Artificial Intelligence General Science (JAIGS), 5(1), 13-21.
Zhao, Peng, et al. (2024). Task allocation planning based on hierarchical task network for national economic mobilization. Journal of Artificial Intelligence General Science (JAIGS), 5(1), 22-31.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
ARK
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Ziyi Zhu, Zeyu Wang, Zhizhong Wu, Yiqian Zhang, Shi Bo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Research Articles in 'Applied Science and Biotechnology Journal for Advanced Research' are Open Access articles published under the Creative Commons CC BY License Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. This license allows you to share – copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format. Adapt – remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially.










